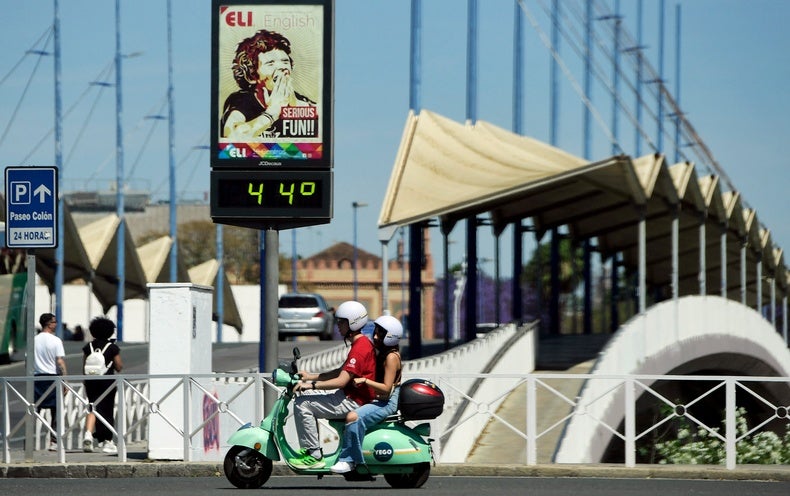
Texas is no stranger to scorching summer months heat, but even Texans are rising weary of a big “warmth dome” that has parked by itself around the location and will retain temperatures soaring to perhaps fatal extremes in the state for the 3rd 7 days in a row.
Several places in Texas have professional days of triple-digit temperatures. On Sunday the Nationwide Temperature Assistance (NWS) office for Austin and San Antonio reported in a tweet that the city of Del Rio, Tex., on the border with Mexico, experienced observed 8 straight days with day-to-day report highs, all in the triple digits. In central Texas, San Angelo strike 112 degrees Fahrenheit on Sunday, very easily topping that date’s earlier document of 106 degrees F in 1994. “It’s really hard to think that just a 7 days ago, 112° would’ve been our all-time file superior and now it is just a different working day of 110° warmth to incorporate to the depend,” the NWS San Angelo office wrote on Twitter. (The city set an all-time high of 114 degrees F the past 7 days.)
This relentless, history-breaking heat wave bears all the hallmarks of what researchers be expecting to see with climate adjust: particularly, heat gatherings that are much more extreme, very last lengthier and happen more often.

��️��️Here’s however one more way to say, “It is been incredibly hot.” We’ve had extreme heat warnings for two months straight! We’ve broken a number of significant temperature data and had unbelievably higher dewpoint values. �� #txwx #stxwx #ItsHot pic.twitter.com/rfm4rPkfBO

— NWS Corpus Christi (@NWSCorpus) June 26, 2023
The stifling temperatures that have been baking Texas and Mexico because early June are happening mainly because of a higher-tension system—also called a ridge—which has “gotten entrenched, and it seriously hasn’t budged substantially,” claims Andrew Quigley, a meteorologist at the NWS workplace for Austin and San Antonio. Significant-force units feature sinking air, which compresses and turns into warmer. These devices also convey apparent skies, letting as a result of lots of daylight that further more raises surface area temperatures. When these a method receives stuck in excess of an area, it’s called a “heat dome.” One more heat dome made more than the Pacific Northwest and Canada in late spring, supporting fuel wildfires that have despatched smoke down over big sections of the U.S.
So why has the present-day Texas heat wave dragged on for so long? At the time a warmth dome has dug in, it usually takes a huge thrust from the jet stream or one more relatively solid process better up in the atmosphere to dislodge it—and “we just have not noticed any kind of influences like that crossing this component of the state,” Quigley states. The most recent guidance from forecast types indicates the warmth may possibly not budge till sometime soon after July 4.
And it isn’t just the heat—it’s also the humidity. Texas’s proximity to the Gulf of Mexico means there is ample dampness in the air, and superior humidity raises the warmth index (a measure of what temperatures experience like to the human body). Lots of destinations have witnessed a document variety of hours with dangerously large warmth index readings, according to the NWS. A significant chunk of Texas has expert warmth indexes in the 110s or 120s F. Corpus Christi, Tex., positioned on the Gulf of Mexico, noticed the heat index get to 125 degrees F. The metropolis has also noticed 14 times in a row of abnormal warmth warnings. “We’ve considerably surpassed the most too much warmth warning times that we have experienced in a calendar year,” claims Penny Harness, a meteorologist at the NWS Corpus Christi place of work.
Even in a aspect of the nation that is no stranger to sultry summers, this extended severe warmth is hazardous, specially to people today who work outside—such as building workers and farm workers—as perfectly as unhoused men and women, the pretty youthful, the aged and these with specific medical ailments, these types of as coronary heart ailment and bronchial asthma. “It’s harmful for men and women since you just really don’t have that opportunity to get better if it’s just day after day” of excessive heat, Harness claims.
In the U.S., the amount of heat-related diseases and fatalities has been escalating since the 1980s. Warmth is deadlier than a lot more fearsome-sounding weather conditions gatherings these types of as hurricanes, floods and tornadoes—combined. “It’s actually not even close with any other extraordinary,” says Greg Carbin, chief of forecast operations at the NWS’s Weather conditions Prediction Heart.
NWS offices and other officials across Texas have been warning residents to restrict intense outdoor activity, to choose a good deal of breaks (preferably indoors with air-conditioning or at the very least in the shade) if performing outside and to usually drink a good deal of water. “If you’re sensation thirsty,” Quigley claims, “it’s now as well late.”
Local weather adjust is amplifying this and other heat functions, as international ordinary temperatures are by now about two degrees F (a single degree C) higher than in preindustrial moments. With the earth however warming as individuals continue on to burn up fossil fuels that release warmth-trapping greenhouse gases, heat waves will continue to take place additional typically, last for a longer period and arrive at larger temperatures. In part mainly because of much more extreme heat waves, an unusually hot summer months in the past is now considered typical. And today’s record scorching summers will feel ho-hum in the future if we do not appreciably curtail greenhouse gas emissions.
There is also some exploration that suggests climate change may perhaps be expanding the likelihood of weather conditions patterns like this sticking in area. The plan is that the rapid warming of the Arctic is altering the jet stream—the fast-moving present-day of air that guides weather conditions systems close to the Northern Hemisphere—in a way that makes these weather styles adhere in position.
In the coming days, the heat dome in excess of Texas may shift a little, bringing hotter weather to some encompassing states. “There’s not much of a split in sight,” Carbin states.
Sooner or later the sample will dislodge—though that does not appear to be most likely right up until someday following week—and temperatures in Texas will drop back again to the additional seasonable higher 90s, which absurdly “will be some sense of reduction,” Quigley suggests.