Venomous Snakes May Spread into Susceptible Communities mainly because of Local weather Adjust
Deadly bites could surge as venomous snakes migrate into unprepared international locations as the weather changes
African eco-friendly bush viper (Atheris squamigera).
Mark Kostich/Getty Photographs
From fish shifting poleward in the oceans to mountain-dwelling birds and frogs inching upslope, animals all about the globe are being compelled by rising temperatures to depart their historic habitats in search of the problems they’ve long been adapted to. Including to this list, new exploration warns that weather adjust is now pushing venomous snakes out of their usual ecosystems—and into new, unprepared parts where they will pose a even bigger public overall health risk.
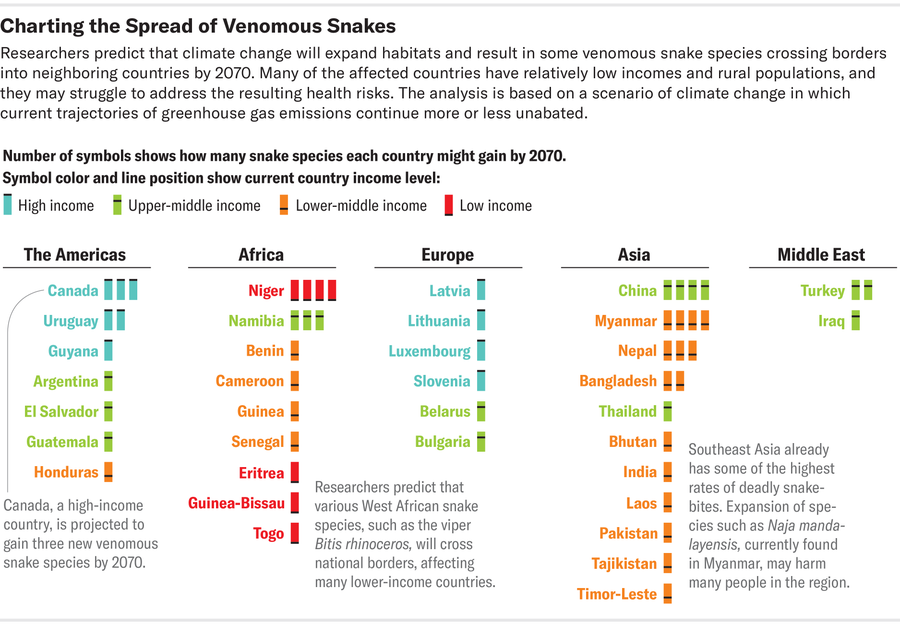
For a new research in the Lancet Planetary Wellbeing, scientists paired local climate products with data on a variety of venomous snake species’ present-day habitats to forecast in which and when they will most likely begin moving. If individuals really don’t cut down greenhouse gas emissions, quite a few snake species will get rid of their habitats and shift into spots wherever they are at this time not observed by 2070, the review concluded.
Most of this movement will happen all-around sub-Saharan Africa and specific sections of Asia—regions that now have the world’s optimum snakebite incidence and mortality rates. The nations around the world that will see the largest boost of species from neighboring nations around the world are China, Myanmar and Niger (with an estimated 4 news species every single) and Nepal and Namibia (with a few every single). “Some areas are heading to have improved climatic disorders for snakes,” states study co-creator Pablo Ariel Martinez, an ecologist at Federal College of Sergipe in Brazil. He and his workforce discovered that savannas, grasslands and deserts will obtain venomous snake species, even though tropical rain forests will get rid of some.
On supporting science journalism
If you might be making the most of this article, consider supporting our award-profitable journalism by subscribing. By acquiring a subscription you are helping to guarantee the foreseeable future of impactful tales about the discoveries and ideas shaping our entire world right now.
A few viper species—Bitis rhinoceros, Vipera aspis and Vipera ammodytes—are expected to deal with the most new habitat. These snakes typically inhabit dry, rocky spots with limited vegetation and exhibit a choice for agricultural land about forests. As farming expands and temperatures grow to be warmer and drier, these species are probable to find a lot more suited habitat around rural communities.
Rural communities in countries these kinds of as Bangladesh, Nepal and Pakistan, in which snakebite is currently a important issue, are at possibility as new snake species shift in.
Abul Faiz, an specialist in tropical medication, who previously co-chaired the Earth Health and fitness Organization’s doing work group on snakebite, clarifies that rural locations of Bangladesh, where by he is from, are more susceptible because of the way folks make a residing. “People are at threat when working in the fields, about their homes and at night time although sleeping on the flooring of badly crafted properties,” he suggests. Every yr around 400,000 men and women in the state are bitten by venomous snakes, and 95 p.c of these incidents come about in rural communities. Very poor health-related infrastructure, transportation difficulties and a shortage of skilled clinicians exacerbate the difficulty. “Medical medical professionals in rural hospitals are worried to use antivenom [because of a lack of instruction] and are not very well educated [on it],” adds Faiz, who was not concerned in the new review. Similar scenarios exist in Pakistan, India and Brazil together with a reliance on regular healers and unproven herbal cures.
Most snake venoms consist of a mixture of poisonous substances that can liquefy bodily tissues and wipe out organs, paralyze breathing and other vital units or prompt inside bleeding. The blend of venom varieties varies both inside of and in between species, that means health care professionals need the unique antivenom for a supplied species. But creating antivenoms is arduous and tough it typically consists of injecting a little amount of money of venom into animals these kinds of as horses or sheep and then extracting the antibodies they generate in response—and manufacturing depends on the offer of venom, which has to be extracted by hand from deadly and occasionally exceptional snakes.
The extremely variable timing of symptom onset complicates things as properly. Right after a pit viper bite, for instance, it may well take anyplace from 30 minutes to an hour before redness and inflammation even seem at the bite web-site. But a black mamba chunk can kill in as very little as 20 minutes. Caregivers need to know how a great deal time they have in each snakebite situation.
Some of the communities that are most vulnerable to new snake species may perhaps also be the the very least ready. “Snake species have no political barrier, but the availability of antivenoms is dependent on the state,” Martinez states. Most countries stock antivenoms personalized to the species generally encountered inside of them and will possible deficiency effective antidotes against the venom mixes of freshly released snakes.
Extraordinary weather conditions events this sort of as floods can also worsen the trouble. Previous investigate in Southeast Asia has proven that snakebite incidents increase for the duration of the monsoon season this is since snakes and individuals the two seek out shelter absent from floodwaters and become extra most likely to experience every other. As local weather adjust improves flooding, the danger of snakebite may perhaps rise even further.
Regardless of these threats to people, the researchers emphasize that venomous snakes are important components of ecosystems as predators of animals these types of as rats and insects. And some compounds identified only in venom have opportunity health-related works by using unrelated to snakebite, this kind of as cytotoxins with anticancer possible or proteins that can be utilised in antihypertensive drugs. If this sort of snakes completely disappear, “we close up dropping a group of organisms that are beneficial from a human standpoint, economically and pharmacologically,” claims Talita Amado, a previous postdoctoral researcher at the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Study and co-writer of the new examine.
But handful of communities would see any upside to an influx of fatal snakes, Faiz notes, which is why educating communities and supplying additional methods is an essential stage towards mitigating fears and preparing folks. “It’s not just about obtaining antivenom,” he says, but also about coaching health staff, making use of community-led avoidance strategies and improving upon health care amenities. Amado adds that preserving up to date databases of antivenoms and avoidance tactics will be crucial in serving to communities act speedily when snakes strike. “Poisoning is going to transpire,” she says. “What will avert folks from being much more or considerably less negatively impacted will be local prevention.”















