Finding out Mouse Reactions to an Optical Illusion Can Instruct Us about Consciousness
A analyze of mice begins to unravel how the mind receives tricked by a specific optical illusion
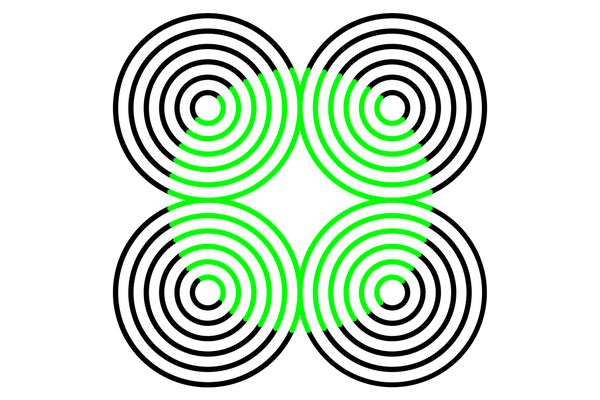
The new examine investigated the notion of brightness in mice by searching at how they responded to an optical illusion called the neon-colour-spreading illusion, an instance of which is illustrated above.
Optical illusions enjoy on the brain’s biases, tricking it into perceiving images differently than how they truly are. And now, in mice, scientists have harnessed an optical illusion to reveal concealed insights into how the mind processes visual information.
The study targeted on the neon-coloration-spreading illusion, which incorporates designs of thin strains on a good qualifications. Sections of these traces are a distinctive shade — such as lime inexperienced, in the instance higher than — and the mind perceives these strains as aspect of a good form with a distinct border — a circle, in this situation. The shut shape also seems brighter than the lines encompassing it.
It can be perfectly set up that this illusion triggers the human brain to falsely fill in and understand a nonexistent define and brightness — but you can find been ongoing discussion about what is heading on in the mind when it occurs. Now, for the to start with time, researchers have shown that the illusion is effective on mice, and this allowed them to peer into the rodents’ brains to see what’s going on.
On supporting science journalism
If you are savoring this article, contemplate supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By obtaining a membership you are supporting to make certain the long run of impactful tales about the discoveries and strategies shaping our planet nowadays.
Specially, they zoomed in on section of the mind termed the visible cortex. When gentle hits our eyes, electrical alerts are despatched via nerves to the visible cortex. This area processes that visible details and sends it on to other areas of the brain, making it possible for us to perceive the globe all over us.
The visible cortex is designed of 6 layers of neurons that are progressively numbered V1, V2, V3 and so on. Each layer is responsible for processing unique attributes of visuals that strike the eyes, with V1 neurons managing the very first and most standard layer of information, while the other layers belong to the “better visible locations.” These neurons are responsible for extra complex visible processing than V1 neurons.
Until finally now, researchers have debated the extent to which V1 neurons answer to illusory brightness, this kind of as the brightness people today understand when wanting at the neon-coloration-spreading illusion. In a sequence of lab experiments in mice, researchers have now shown that these neurons perform a essential role in this process and that their activity is also tempered by suggestions from V2 neurons. So you can find a volley back and forth amongst these different layers of the visible cortex.
This knowledge may well bolster our comprehending of consciousness, the researchers claimed in a paper revealed April 23 in the journal Nature Communications.
“The noticed partnership involving V1 and V2 in processing the illusion implies that consciousness is a best-down procedure,” as opposed to a bottom-up method, co-author Masataka Watanabe, an associate professor in the division of techniques innovation at the College of Tokyo, told Reside Science in an e mail.
This is an alternative edition of the neon-shade-spreading illusion. In this circumstance, the mind perceives the coloured blue traces as belonging to a blue circle, but in fact, the background is however white and the blue lines don’t variety a closed form.
Top-down processing refers to the way our brains interpret our environment by having prior encounters into account, alternatively than only relying on visible stimuli on your own. By contrast, pure bottom-up processing would consider the diverse functions of an graphic and snap them collectively like puzzle items, producing a coherent photograph with out input from a person’s memory.
Other studies have implied that consciousness is a top rated-down-system, but this mouse research delivers direct proof for it, Watanabe reported. The respond to is just not black and white nevertheless, as some argue that consciousness probable occurs from a combination of equally.
What is the new evidence? In the examine, mice ended up revealed a mixture of neon-coloration-spreading illusions and other, comparable-seeking styles that did not bring about the illusion. Simultaneously, Watanabe and colleagues measured the exercise of neurons in the rodents’ brains with implanted electrodes.
The workforce also calculated no matter whether the mice noticed the illusions as vibrant by assessing how a lot the pupils in their eyes dilated or constricted. This response matched that witnessed in people when we understand changes in light-weight levels.
V1 neurons reply to each illusory and non-illusory visuals, but they just take lengthier to reply to the previous. This supports the idea that V1 neurons have to have feed-back from bigger visual regions to procedure these types of illusions, the crew documented.
The scientists then tried out experimentally inhibiting the action of the larger visible location neurons, finding that V1 neurons were less possible to reply to the illusions. This presented further more proof that a increased-level comments loop is required to understand the illusion.
Likely forward, the team ideas to conduct even more scientific tests in which they are going to mess with the exercise of larger visual area neurons in mice, Watanabe claimed. They hope that this will drop more light on the neural mechanisms fundamental consciousness in mice, and by extension, in humans.
Copyright 2024 LiveScience, a Upcoming organization. All rights reserved. This content may perhaps not be revealed, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.