Neither Crops nor Animals, These Ocean Organisms Safeguard Their Ecosystems in opposition to Heat Waves
Mixotrophs, which have features of both equally animals and vegetation, could assist blunt the effects of maritime heat waves on ocean ecosystems
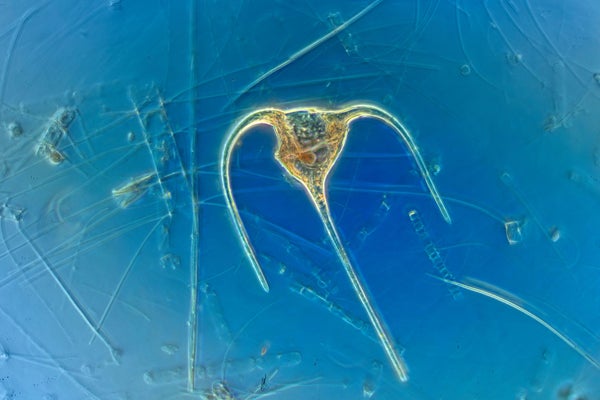
Micrograph of maritime phytoplankton.
Scenics & Science/Alamy Stock Photograph
For just about two several years starting in 2014, the waters alongside North America’s Pacific Coast endured the premier and longest-long lasting maritime warmth wave ever recorded. Many species were devastated by ocean temperatures up to 2.4 levels Celsius (4.3 degrees Fahrenheit) bigger than regular. Kelp forests off northern California declined by extra than 90 p.c, an believed million or far more seabirds died, and fisheries closed up and down the coast, costing some fishing communities hundreds of millions of bucks. But 1 unassuming group of organisms managed to climate the unrelenting warmth fairly well—by breaking the guidelines of biological separation concerning animals and plants.
Now new research indicates the adaptable life-style of these organisms could make them important to the survival of ocean ecosystems as local climate improve proceeds to crank up the warmth.
Just one of the initial points numerous persons find out in biology class is that a essential line can be drawn amongst two of Earth’s main varieties of daily life. On 1 facet there are the autotrophs, these kinds of as crops, which mostly use photosynthesis to make food items out of air, water and minerals, applying strength they get from light-weight. On the other are heterotrophs, such as animals, which are not able to photosynthesize and so need to eat other organisms to get vitality. That division is a practical starting up point—but like any simplified narrative, it leaves out a good deal. All above the earth there are organisms referred to as mixotrophs that blend both of those of these strategies.
On supporting science journalism
If you are enjoying this short article, think about supporting our award-profitable journalism by subscribing. By acquiring a membership you are assisting to make sure the foreseeable future of impactful tales about the discoveries and strategies shaping our world now.
Many species of mixotrophs type a major portion of oceanic plankton and are essential to marine food items webs. Mixotrophic plankton these types of as ciliates and dinoflagellates can get power by consuming some of the smallest one-celled plankton, which are too little to be competently applied as food by larger species. These mixotrophs can enjoy the advantages of both of those photosynthesis and consumption of prey. Some are pure photosynthesizers that dietary supplement that vitality by having, whereas many others can combine photosynthesizing phytoplankton into their have bodies. The mixotrophs are in turn eaten by bigger plankton species these as copepods and krill, which then turn out to be prey for numerous fish, seabirds and marine mammals.
The new study, published not too long ago in Aquatic Microbial Ecology, identified that mixotrophic species created up a larger sized share of the plankton in the Gulf of Alaska throughout two main heat waves (from 2014 to 2016 and in 2019) than in a long time with typical ocean temperatures. And even amid the mixotrophs, the additional generalist species—those equipped to feed on and variety relationships with a wider vary of phytoplankton—survived the heat waves better than a lot more specialized types. “Having extra than a single way to dwell in your back again pocket is in all probability particularly beneficial in a extremely variable setting,” states Suzanne Strom, senior marine scientist at Western Washington University and the paper’s lead writer.
The examine reveals that these adaptable mixotrophs can be vital to the complete Gulf of Alaska ecosystem in warmth wave decades for the reason that they assistance to mediate a main consequence of marine warming: increased stratification, or the separation of ocean water into distinct levels. This result can protect against the mixing of nutrition that would usually gas sturdy aquatic ecosystems. In particular amid somewhat extended-lasting heat waves, stratified waters can lead to significant phytoplankton blooms by trapping vitamins at the surface area. As soon as people vitamins and minerals are eaten, the blooms dissipate, leaving an place of depleted oxygen, and the stratification stops much more vitamins from soaring to the surface area to restart the cycle. This can bring about die-offs amid fish and other species.
“That’s when the mixotrophs seriously develop into essential in that process,” states Diane Stoecker, a professor emerita at the University of Maryland’s Center for Environmental Science, who was not involved in the latest paper. These organisms’ combined strategy—both consuming meals all over them like an animal and producing their own electrical power like a plant—makes them additional successful in these types of lean occasions. That means foodstuff webs on the verge of collapse from a lack of new vitamins may be capable to hold likely lengthier when mixotrophs are current than they could without the need of them.
As local weather alter helps make marine warmth waves much more regular and critical, it is significant for scientists to comprehend what species or procedures might supply a buffer for ecosystems. The new analyze displays that as lousy as current maritime heat waves have been, it could have been a great deal worse without the need of mixotrophic plankton and the resilience they lend to the maritime foodstuff webs of northern seas.
“These marine warmth waves offer insights into what potential warm ailments may possibly appear like,” states Chris Free, a College of California, Santa Barbara, ecologist who was not associated in the new examine. “While they introduce a good deal of turmoil, they are also seriously essential to research because they enable us prepare for the foreseeable future by knowing what the location will seem like when it does develop into hotter.”