Europe’s Mars Rover Will Use New Nuclear Electric power Source
The radioactive unit will assist to deliver Europe’s very first Mars rover to the planet’s area
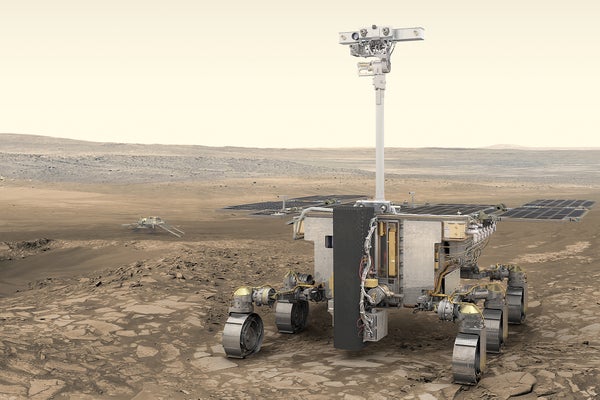
An artist’s perception of ESA’s ExoMars rover, Rosalind Franklin.
Europe’s forthcoming Mars mission will use a pioneering nuclear-driven machine that harnesses the radioactive decay of americium to preserve its components warm — a 1st for spacecraft.
The European Space Company (ESA) declared the ideas on 16 May perhaps, alongside facts of an settlement with NASA that crystallized the US agency’s contribution to the extended-delayed mission, which will produce Europe’s initially Mars rover, called Rosalind Franklin. ESA was initially working with Russian space company Roscosmos on the mission, but cancelled the partnership in 2022 soon after Russia invaded Ukraine.
Units that harness the warmth manufactured by the decay of radioactive elements, identified as radioisotope heater units (RHUs), let spacecraft to run without relying on electricity created by solar panels to warm them. ESA has traditionally relied on US or Russian associates to give RHUs that use plutonium-238 for missions, but due to the fact 2009 has been functioning on its personal programme to build radioisotope heaters, as very well as batteries that offer electrical energy.
On supporting science journalism
If you are enjoying this post, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By paying for a subscription you are supporting to ensure the long run of impactful stories about the discoveries and suggestions shaping our environment right now.
The European RHUs will heat components in the mission’s landing system, which deploys the rover on to the Martian area. The lander powers the rover just before it exits the platform and opens its solar panels. So extending the lander’s lifetime offers back again up in case there are problems in deploying the rover, claims Orson Sutherland, ESA’s team chief for Mars Exploration, based mostly at the European Room Exploration and Technologies Centre (ESTEC) in Noordwijk, the Netherlands.
Americium decay
ESA’s heater models will not only be a initially for Europe, but the first any place to use americium-241, a by-product or service of plutonium decay that packs much less power for each gram than its predecessor. But americium-241 is more considerable and less expensive, indicating that even if the RHUs need additional of the isotope to run, they may well be significantly less costly general. “Developing and launching a European RHU will be a first for ESA and a main accomplishment,” suggests Sutherland.
The Rosalind Franklin rover is uniquely geared up to lookup for traces of historic daily life on Mars, with a 2-metre drill that lets it to burrow deep beneath the Martian surface area. But the mission was originally slated for start in 2018 and had previously been delayed by specialized difficulties and the COVID-19 pandemic even just before tensions escalated with Russia.
ESA experienced to radically rethink the mission to proceed without the involvement of Roscosmos, which was meant to build the lander. That led ESA to produce a new European-designed lander and depend on NASA to fill the remaining holes in the mission plan. According to the agreement, NASA will present potential to start ExoMars in 2028, as properly as supply braking engines for the lander. NASA will also deliver radioisotope heater units for the rover.
Long term batteries
The americium RHUs are staying made as portion of the European Devices Utilizing Radioisotope Energy (ENDURE) undertaking. Since the equipment include radioactive components, they involve certification in advance of start. The collaboration is doing the job on satisfying start-basic safety requirements in time for 2028, suggests Richard Ambrosi, a physicist and specialist in place-ability techniques at the University of Leicester, aspect of the Uk-primarily based workforce foremost advancement of the unit.
By the close of the ten years, ENDURE aims to have developed americium batteries capable of giving energy to a spacecraft alternatively than just warmth, in time for a collection of ESA Moon missions in the early 2030s. Whilst an RHU works by using the warmth the natural way developed by radioactive decay, a nuclear battery — acknowledged as a radioisotope thermoelectric generator — converts that warmth into electrical electric power.
The Nationwide Nuclear Laboratory, primarily based in Sellafield, Uk, will make the americium pellets essential for the heaters and batteries from put in nuclear gas from the civil British isles energy crops.
ESA getting its possess heating units will let the company to expand its exploration horizon, claims Sutherland. “The ability to continue to keep flight techniques warm in shaded locations, these types of as craters, or all through the night will let formerly inaccessible spots to be explored and increase mission life time,” he claims.
This write-up is reproduced with permission and was to start with published on May well 21, 2024.