Adolescence is a impressive period of time of advancement and studying, a time when youths discover and adapt to improvements in their social worlds and start out to sort a sense of who they are and hope to be. It is a time when they initially demonstrate a extraordinary adaptability to the unique cognitive, emotional, bodily, social and sexual demands positioned on them as they changeover from dependence on their mothers and fathers or caregivers to relative independence. It is also, regretably, a time when the emergence of most psychological health troubles peaks.
The most prevalent mental health considerations struggling with adolescents currently are anxiousness disorders, and their prevalence has been growing for the past decade. A study of tens of 1000’s of teens showed that this prevalence increased about 30 to 40 per cent concerning 2012 and 2018, and primarily based on proof from teens from Germany, it rose an additional 70 per cent throughout the very first couple of many years of the COVID pandemic. Nevertheless anxiousness issues in young folks are mostly undertreated.
The only proof-primarily based behavioral treatment plans for stress and anxiety are cognitive-behavioral therapies (CBTs). They contain identifying triggers of anxiousness and then desensitizing the affected person to them by means of coping techniques these types of as constructive believed reframing or respiratory workout routines, together with recurring publicity to the triggers in a secure environment. Whilst CBT is the most proven treatment method for adolescent anxiousness, not all youths who try it experience reduction. Amid people who do, several are unsuccessful to sustain enhancements over time. A mere 20 to 50 per cent of individuals treated for nervousness devoid of medicine throughout adolescence keep on being in remission 6 a long time soon after initial CBT. The implications can be very long-lasting and severe. Still left untreated, panic can lead to much more significant chronic illnesses these as melancholy and material use problem later on in lifetime, increased susceptibility to physical ailments and, in severe circumstances, suicide.
On supporting science journalism
If you’re savoring this post, take into consideration supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By buying a subscription you are aiding to make sure the potential of impactful tales about the discoveries and concepts shaping our planet currently.
Fortunately, new discoveries about the adolescent brain are demonstrating promising paths ahead for the cure of anxiousness. Current exploration gains from rapidly advancing imaging systems that can reveal patterns of neural exercise and fascinating potential avenues for intervention. These modalities have currently offered entry to the internal workings of the acquiring mind in laboratory animals and teenagers, and scientists hope they will lead to new approaches in scientific observe that consider into account the special adjustments in the human mind through adolescence. By focusing on the building brain and the behaviors it generates early on in lifetime, we may possibly be far better equipped to change stress and anxiety-linked reminiscences, determine cues and cases that aid to reduce indications, and mitigate the adverse consequences of panic for young people today before they grow to be a a lot more long-term affliction in adulthood.
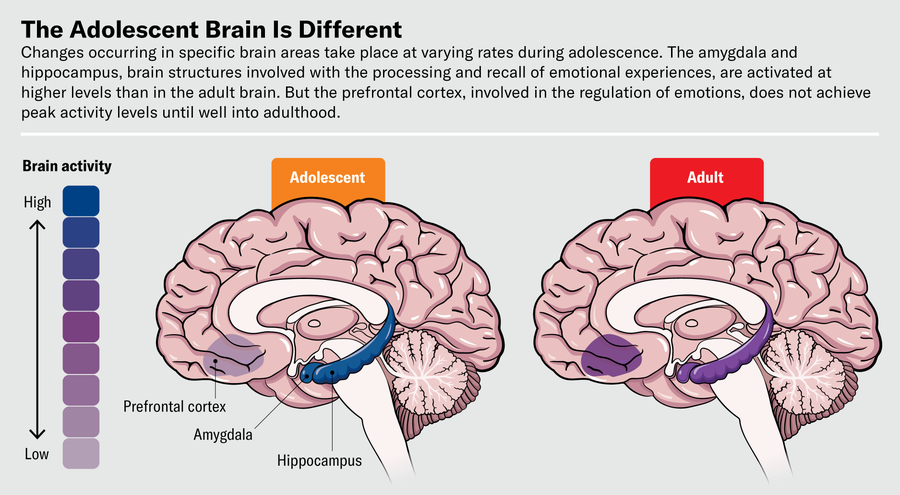
In the past two many years we have figured out that the adolescent mind undergoes notable modifications in composition and functionality, and these variations are distinct from individuals noticed in the course of early childhood and adulthood. They are localized, meaning certain mind places modify before in development than many others. Regions associated in feelings, this sort of as the amygdala and the hippocampus, show peak structural and functional changes during the teenager a long time. For illustration, throughout adolescence the amygdala’s volume boosts (a structural modify), and so does the way the amygdala is activated by certain psychological encounters (a useful alter). In contrast, mind locations and circuitry linked with the regulation of thoughts, thoughts and actions—the prefrontal cortex, for instance—change more slowly, with development continuing well into adulthood. These discrepancies in developmental timing may possibly direct to an imbalance in conversation amid mind locations, permitting a single region to prevail around a further in an adolescent’s determination-generating. Appropriately, in emotionally billed or threatening circumstances, early-producing emotional spots “win out” above later-developing types, driving some of the reactions and responses linked with the behaviors of anxious and volatile teenagers. These regional variations might have served an evolutionary objective. They have been linked to heightened sensitivity to emotional and social data that may be critical for reproductive achievement and the survival of the human species. Regretably, these similar imbalances have also been involved with elevated reactivity to strain and larger susceptibility to stress problems.
A main emotion related with anxiousness disorders is dread. Though dread is an adaptive response to threats and thus crucial for survival, persistent fear prolonged immediately after a risk has been eliminated can direct to a pathological condition of anxiety. Men and women with nervousness disorders have problem determining when earlier threatening cases have become secure, and they may well overgeneralize by imagining that a destructive encounter in 1 problem will recur in other eventualities.
Many years of animal and human research have recognized the standard mind circuitry for remembering an obtained fear in adults. The amygdala is essential to developing a anxiety memory, and parts of the prefrontal cortex are included in reducing the toughness of anxiety memories—a process recognised as extinction. The two the amygdala and the prefrontal cortex are hugely interconnected with a third location, the hippocampus, which plays a job not only in concern extinction but also in deciding how we practical experience anxiety in various conditions. In individual, the hippocampus provides information and facts about the bordering ecosystem to assist an unique make your mind up whether or not a presented situation is a lot more very likely to existing a danger (for instance, a bear in the woods) or an absence thereof (a bear at the zoo). Considerably of this circuitry is conserved across various species, enabling the translation of primary animal research to remedies in humans.
Just lately researchers have targeted focus on panic memory and extinction in the course of adolescence. These reports present that adolescents, like preadolescents and grown ups, are able of attaining a worry memory, but they are much less in a position to extinguish all those memories than people today in other age teams. After remaining uncovered to a couple of straightforward pairings of a neutral stimulus (a colored sq.) with an aversive stimulus (a loud sound), youngsters, adolescents and adults alike show a fear response, measured by sweat gland action, to the colored square even when the loud noise no more time transpires. When preteen small children and older people are then presented continuously with the colored sq. devoid of the loud sounds, they start out to see the sq. not as anything predicting the threat of the loud noise but relatively as a safe refuge from it—the concern memory is extinguished. Adolescents, even so, keep on to respond fearfully to the coloured sq..
In conditions when fear does get diminished for adolescents, it consistently returns with the passage of time. The finding that adolescents “learn” to extinguish concern significantly less readily than younger or more mature people today has been replicated in scientific tests across species (mice, rats and individuals). Most notably, in the course of this developmental time period, the amygdala is much extra involved in sustaining the fear memory than the prefrontal cortex is in initiating the extinction process. A reduce capacity to initiate dread-extinction mastering is considered to confer a threat for panic. Therefore, adolescents may innately be at better danger.
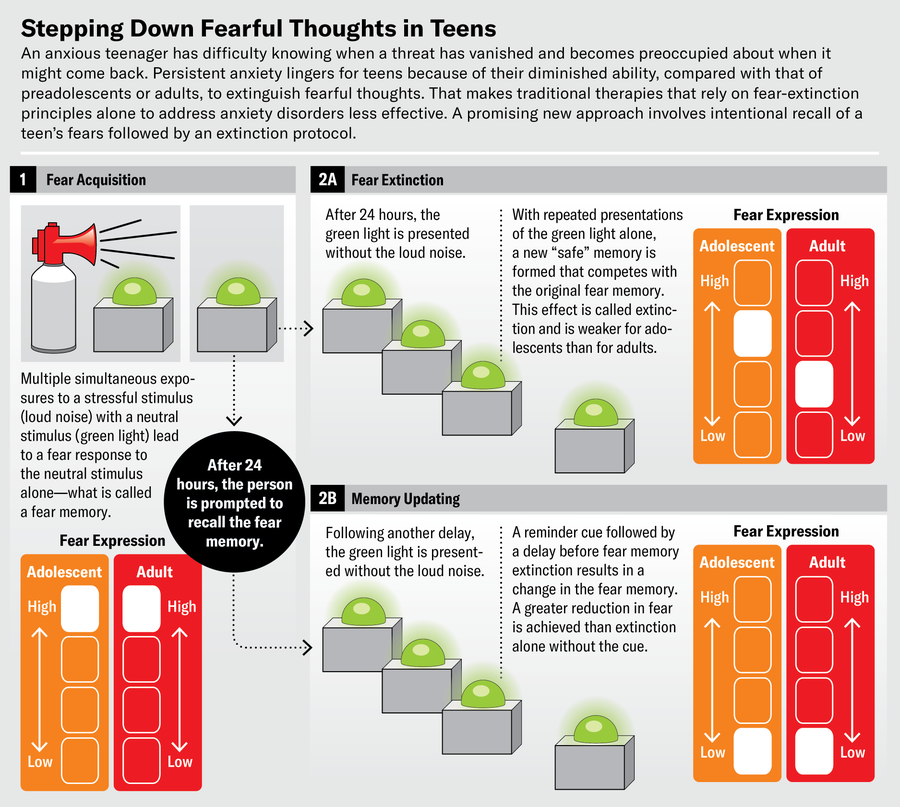
The discovery of distinctions in fear-extinction actions and brain circuitry in the course of adolescence has essential implications not only for understanding the opportunity for enhanced susceptibility to anxiety ailments but also for deciding upon treatment method possibilities. Behavioral therapies these types of as CBT entail figuring out triggers of anxiousness, getting coping techniques and undergoing a process of desensitization developed on the rules of concern extinction. But through adolescent dread extinction, the involvement of the prefrontal cortex, which is affiliated with the organizing and handle of habits, is diminished—which indicates that for adolescents, the usefulness of regular publicity-primarily based CBT could possibly also be diminished. Jointly, these facts elevate the problem of how we must tailor therapies for the acquiring mind. Specially, how could we use what we know about the brain’s concern circuitry and the enhancement of fear learning during adolescence to guide interventions that could be far more productive in altering teens’ panic recollections?
One technique will involve conceding the delayed maturation of the prefrontal cortex and circumventing the region in therapy. Relatively than relying on prefrontal-based extinction understanding, we have tested an alternate strategy referred to as memory reconsolidation updating. Memory reconsolidation is primarily based on the principle that reminiscences are dynamic, not static. Each individual time a memory is retrieved, it receives modified. Reactivating a panic memory by presenting a reminder of the dread stimulus opens a time-constrained window all through which the memory by itself turns into inclined to disruption and modify.
Studies in both equally humans and rodents recommend that worry-memory updating is mediated by modifications to the memory in the amygdala. In contrast to the prefrontal circuitry, which carries on to display developmental variations into younger adulthood, the amygdala undergoes peak maturation for the duration of midadolescence.
These results advise that 1 way to assistance adolescents overcome pathological dread is to introduce what is called a reminder cue to retrieve the memory, followed by a delay ahead of subsequently extinguishing it. In our lab, we tested this concept in equally healthier adolescents and grown ups by evaluating their retention of a worry memory just after extinction with and devoid of a preceding reminder cue. We observed that even however adolescents usually display diminished panic extinction relative to grownups, all those who were prompted to retrieve the fearful memory a number of minutes just before extinction mastering confirmed a spectacular reduction in panic the future day in contrast with these who underwent only extinction understanding. In fact, all those adolescents’ panic recollections diminished to the exact same degree as noticed in grown ups.
Traditionally, extinction discovering requires forming a new, competing, secure memory that leaves the initial dread memory intact, meaning it is achievable for people fearful views to return later on. The present findings, nonetheless, recommend that with memory reconsolidation updating, the initial fear memory is altered. As a result, the reconsolidation technique has the probable to both equally lessen worry at the time of procedure and lessen the likelihood that it will return.
This investigation is thrilling due to the fact it indicates a path to the medical use of reconsolidation updating. Straightforward modifications to present publicity-dependent CBT methods may verify effective in decreasing triggers of fear and anxiousness in adolescent clients. This approach could entail a step as simple as the therapist reminding people why they are there when they get there for their appointment—the equal of the reminder cue and worry-memory retrieval in the lab setting. Then the therapist could expend numerous minutes creating a harmless rapport with the patient even though ready for the memory to enter a labile state during the reconsolidation-updating window. Desensitization with exposure treatment could then start throughout the time in which the updating system usually takes area. The present-day variable efficacy of CBT in adolescents with anxiety disorders may possibly be explained by the actuality that some clinicians previously use strategies that inadvertently faucet into parts of reconsolidation updating.
Latest attempts to incorporate reconsolidation-updating strategies in managing adult people with anxiousness and trauma-related diseases have yielded some accomplishment, but to day they have not been utilized with adolescent people. The studies in grown ups present small- and extensive-term reduction of signs and symptoms, primarily for sufferers with unique phobias and submit-traumatic tension ailment. Though far more fundamental and medical investigation is essential, this technique would seem promising.
Another system that may well support adolescents extinguish a worry memory requires the use of basic safety cues that sign there is nothing to be worried of. In an experimental setting, a basic safety cue can be a basic stimulus—a image or a sound—that is distinguishable from and regularly contrasted with a worry cue. Outdoors the lab, security cues appear in numerous varieties and are possible to be a stimulus unique to the particular person: a compact personalized item, a photograph of a loved one particular, a certain scent. We and others have shown that in people and rodents alike, protection cues act by recruiting mind locations that exhibit elevated exercise in the course of adolescence, such as the amygdala and the hippocampus. The anterior aspect of the hippocampus in distinct displays a sturdy raise in action when a security cue is offered together with a concern cue the degree of action corresponds to the reduction in worry. Moreover, security cues rely fewer on the prefrontal cortex than do other sorts of dread regulation, these as extinction, highlighting the achievable benefit of using a protection cue–based strategy for anxiousness through adolescence.
It is not possible to avoid all triggers of extreme worry and anxiousness, so it is vital that patients do not come to be extremely reliant on protection cues to the detriment of understanding other coping competencies. Protection cues may be a important resource for increasing the tolerability of the early stages of cure so that clients do not drop out. Early procedure classes could include things like steerage from the clinician on how to recognize and effectively deploy a protection cue.
As remedy progresses, cues can give clients a way to reduce their worry reaction extended ample to consider the problem and use applications from CBT apply. Even though exploration on integrating security cues into procedure is in its earliest phases, the strategy reveals good assure, particularly for adolescents. Our group just lately shown in mice that intermittently presenting a security cue throughout an extinction protocol led to superior anxiety extinction in adolescent mice than noticed in either adolescent (28 to 50 times) or grownup rodents trained with out a security cue.
The hope for these rising therapeutic ways is that we can tailor present-day anxiety solutions for younger folks by targeting the establishing brain. It is crucial to be mindful of the simple fact that the magnitude and intensity of the worry reaction in people today diagnosed with anxiety are probably considerably increased than the worry evoked by aversive stimuli in lab experiments, which are usually mild, narrowly specific and transient. It is also critical to bear in mind that CBT and antidepressants can handle stress and anxiety proficiently in a lot of persons. Regretably, however, for some, these solutions supply only restricted or temporary positive aspects. Therefore, the most successful kinds of procedure may possibly require a mixture of techniques, which includes desensitization approaches modified to incorporate reconsolidation updating or basic safety cues, probably in conjunction with antidepressants.
The supreme intention is for us to improve latest treatment plans for youths with panic by focusing on the brain throughout a period of time of enhancement accompanied by intensive understanding and, in so accomplishing, increase the quality of everyday living for adolescents both equally in the quick foreseeable future and later in everyday living.







:quality(85):upscale()/2024/07/09/806/n/1922729/2833acbe668d7fc5814e16.08957571_.jpg)






