A Random Influx of DNA from a Virus Aided Vertebrates Become So Stunningly Successful
Insertion of genetic material from a virus into the genome of a vertebrate ancestor enabled the lightning-quick electrical impulses that give animals with backbones their smarts
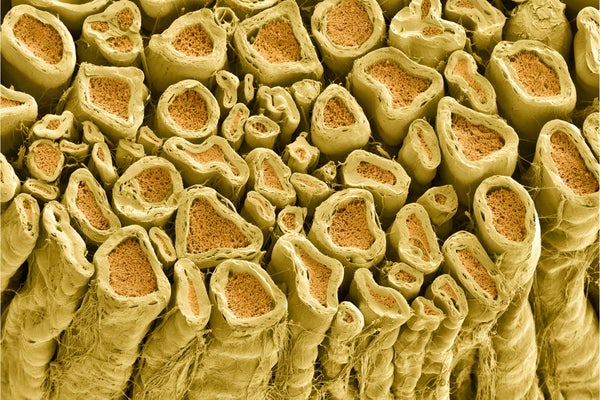
White myelin sheaths around rat nerve fibers.
NIH/Picture Point FR/BSIP SA/Alamy Stock Picture
Charles Darwin proposed that evolution is pushed by gradual versions in organisms that have a survival gain in a changing atmosphere. But College of Maryland evolutionary biologist Karen Carleton claims that scientists have very long grappled with the quandary that “evolution can materialize abruptly, as described by Steven Jay Gould in [the theory of] punctuated equilibrium.” The issue has always been: How does this transpire?
A situation in place is the sudden visual appeal of myelin, the multilayered sheath on nerve fibers that remodeled the way neural impulses are performed and turbocharged the transmission velocity of these impulses. Myelin appears out of the blue in vertebrates, animals with backbones that arose 500 million several years in the past. Not a trace of it is found in the ancestral line that preceded the arrival of vertebrates. A new examine in the journal Cell offers an reply to this long-standing puzzle: the genetic recommendations to make myelin ended up slipped into our vertebrate ancestor’s DNA by an infection with a virus.
Myelin is arguably the most important advance in anxious programs that at any time occurred in the animal kingdom. The terrific enhance in pace of data transmission more than very long distances in the human body is mainly liable for the spectacular leap in cognitive ability in vertebrates, not to mention velocity of motion and agility in pet dogs, dolphins and people, for illustration, when in comparison with invertebrates this kind of as slugs, worms and starfish. Missing myelin, neurons in invertebrates are clustered into groups (ganglia) situated around the overall body buildings they handle or that offer sensory enter. There are ganglia next to just about every swimming leg in a shrimp’s tail, for instance, but in vertebrates, neurons are massed together into just one massive central assembly, the brain. The concentration of billions of neurons into a mind enabled cognitive capabilities nicely over and above those people of invertebrates.
On supporting science journalism
If you’re enjoying this write-up, consider supporting our award-successful journalism by subscribing. By obtaining a subscription you are helping to be certain the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our planet right now.
Curiously, myelin is wrapped about nerve fibers by entirely diverse cells in the system (Schwann cells) than in the mind (oligodendrocytes). If myelin advanced independently in the peripheral and central nervous process, transmission delays in possibly part of the technique would undermine the benefit, like a slow Web relationship hobbling a high-velocity pc. But myelin seems totally fashioned at the same time in the mind and overall body with the evolution of vertebrates. (A single exception is the lamprey eel, the most primitive residing vertebrate, which has no myelin.) All of this raises the concern: Wherever did myelin occur from?
“Myelin evolution is an vital mystery and is fully understudied,” claims myelin researcher Robert Gould at the Maritime Organic Laboratory’s Whitman Investigate Heart, who was not included in the new study. The study stories the involvement of what is named a retrovirus in precipitating the visual appearance of myelination. Gould states that involvement of retroviral RNA in myelination is a surprise—one that really should have essential implications for myelin-relevant ailments, this sort of as various sclerosis.
The central dogma in molecular biology holds that data flows from DNA in the mobile nucleus and is carried outside the house the nucleus to the cytoplasm, the cell’s liquid interior, by another molecule, messenger RNA. The messenger RNA transports a duplicate of the genetic code for a distinct protein to produce to distinct constructions in the cytoplasm that synthesize that protein. Viruses are unable to make proteins on their possess. Alternatively they hijack the molecular machinery of the cells they infect to make all the viral proteins and enzymes needed to crank out new viruses.
Retroviruses these as the HIV virus have out this genetic hacking by reversing the sequence of the gene readout. They inject their RNA into the cells they infect, which serves as the code to make viral proteins. That RNA is transformed into DNA and, like destructive code in a application plan, will get inserted into the cell’s genome. When the mobile reads out that rogue DNA code into RNA, it unwittingly will make the overseas viral proteins.
Dreadful infections and cancers are triggered by viruses corrupting our genome, but sometimes a viral infection has surprising gains, and mutant fragments of viral genes get permanently fixed into the DNA of organisms and can be passed on for generations. These snippets of overseas DNA typically no longer make virus proteins. Even now, they have a potent influence on what genes are browse out to make proteins by binding to DNA locations following to genes and to proteins in the nucleus that manage irrespective of whether or not a gene is expressed. Astonishingly, 40 per cent of the DNA in mammals is made up of remnants of these retroviral bacterial infections.
Myelin biologist Robin Franklin of the Wellcome Genome Campus in England and colleagues report in the new examine that they have determined a retroviral component in all vertebrates except lampreys. The scientists have supplied this insertion into the genome of the frequent ancestor of vertebrates thousands and thousands of a long time back the name RetroMyelin. They have proven that it stimulates the synthesis of proteins that are necessary to earning myelin in both the central and peripheral anxious technique.
When they blocked RetroMyelin in mouse cells in culture—and in zebrafish larva and tadpoles—myelin mainly failed to variety. More experiments exposed how blocking RetroMyelin stymied myelin manufacturing. A important protein in myelin known as MBP is crucial to kind the myelin sheath. The development of myelin usually takes place as a long, tentaclelike extension from a mobile referred to as an oligodendrocyte envelops the nerve fiber.
To have out this approach, MBP on the interior surface area of the oligodendrocyte’s cell membrane pairs up with the exact same type of molecule on the inner membrane of the oligodendrocyte’s elongated tentacle that wraps all-around a fiber. Binding to every other, MBP zips both interior surfaces of the membranes jointly like a folded piece of tape sticking to itself, and this squeezes out all the cytoplasm to form a compact sheath with high electrical resistance. The researchers showed that RetroMyelin latches onto a protein termed SOX10, a transcription component that activates the reading of DNA for the MBP gene. RetroMyelin stimulates SOX10, and in response the cells start generating big quantities of MBP to make myelin.
“This is a extremely exciting research, which identifies an significant aspect in myelination,” says Klaus-Armin Nave, a myelin researcher at the Max Planck Institute for Multidisciplinary Sciences in Göttingen, Germany, who was not associated in the research. “But considered rigorously, the summary that this retroviral an infection was the switch that turned on myelination in vertebrates is based on correlation.” Myelination is a extremely elaborate procedure, he says, which will have to call for quite a few unique proteins and mechanisms of gene regulation. The thriller of myelin may possibly call for more sleuthing: there is, for instance, minimal evidence of MBP in the ancestors of vertebrates. “Where did MBP occur from if there is no DNA sequence for it in prevertebrates?” Robert Gould ponders. “Final proof,” Nave claims, “would be to introduce the retroviral gene into lampreys and see if they variety myelin.”
Retroviruses can be a highly effective motor of evolution, and myelin appears to be one particular of the most extraordinary examples. “It does make feeling that a retrovirus could be involved,” Carleton says. A person hundred decades following the discovery of retroviruses and two hundreds of years just after a 22-year-old naturalist embarked on his 5-yr sailing journey about the world, molecular biology is now tackling the puzzle that Darwin grappled with in his momentous concept of evolution by illuminating how some features seemingly seem out of nowhere.