Pictured below is a real estate venture underneath design in Huai ‘an metropolis, Jiangsu province, China, on April 8, 2024.
Upcoming Publishing | Foreseeable future Publishing | Getty Photographs
BEIJING — China demands to persuade individuals that household selling prices are on their way up in order for financial exercise to pick up, Richard Koo, main economist at Nomura Research Institute, instructed CNBC’s Steve Sedgwick last week.
Business and purchaser urge for food for new loans have had a tepid start to the yr, even though property prices dropped at a steeper speed in January than in February, in accordance to Goldman Sachs’ evaluation.
In other terms, as Koo warned previous year, China could be getting into a “equilibrium sheet economic downturn,” very similar to what Japan expert in the course of its economic slump.
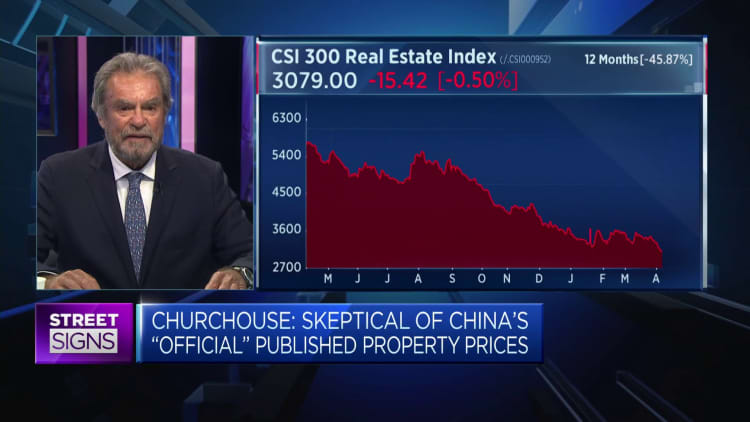
“For them to appear again and borrow revenue, we will need a narrative that suggests, ok, this is the bottom of the charges, the selling prices will begin going up from this stage onwards,” Koo mentioned.
But it’s not apparent whether costs have attained an true bottom nonetheless. Koo and other analysts have pointed out that in China’s policy-driven financial state, residence price ranges have not fallen as a great deal as predicted given declines in other facets of the home market.
Chinese officials have reported that authentic estate continues to be in a period of time of “adjustment.” The country has also been emphasizing new expansion motorists these types of as producing and new electrical power cars.
Genuine estate and related sectors have accounted for at least one-fifth of China’s economy, relying on analyst estimates. The residence current market started its latest slump soon after Beijing cracked down on developers’ high reliance on debt in 2020.
That coincided with the shock from the Covid-19 pandemic.
It also arrives as China’s population has begun to shrink, Koo pointed out — a major big difference with Japan, whose inhabitants failed to get started to slide until 2009, he reported.
“That helps make this narrative, that the rates have fallen more than enough, you should really go out and borrow and obtain houses, even much more difficult to justify mainly because [the] populace is now shrinking,” Koo explained.
Classes from heritage
China’s overall economy officially grew by 5.2% in 2023, the initially calendar year since the finish of Covid-19 controls. Beijing has set a target of around 5% development for 2024.
Nonetheless, lots of analysts have said these kinds of a target is bold devoid of more stimulus.
Chinese authorities have been hesitant to embark on massive-scale support for the financial system. Koo explained an fundamental reason is that Beijing sights its prior stimulus application as a mistake.
About 15 decades ago, in the wake of the world-wide fiscal disaster, China released a 4 trillion yuan ($563.38 billion) stimulus package deal that was in the beginning satisfied with skepticism — and a 70% fall in Chinese inventory rates, Koo claimed.
“It was heading towards balance sheet economic downturn, practically,” he said. “One yr later on, China had 12% expansion.”
But Beijing saved up its stimulus package even right after the nation had attained quick progress, which led to an overheating of growth and speculation, on top of corruption, Koo stated. “That is 1 of the reasons why this government, Mr. Xi Jinping, is continue to unwilling to place [out] a big offer mainly because so quite a few persons think the earlier one particular was a failure.”
Hunting in advance, Koo stated China should really stimulate its overall economy to prevent a harmony sheet economic downturn, and that it must minimize that support once advancement reaches 12%. “At the time the borrow[ing] is coming back again, then you can reduce, but not in advance of.”















