Surprisingly Shaped Bubbles Inform the Tale of Ice’s Development and Composition
Bubbles formed like teardrops, flattened eggs and worms expose ice’s internal existence
Anton Petrus/Getty Photographs
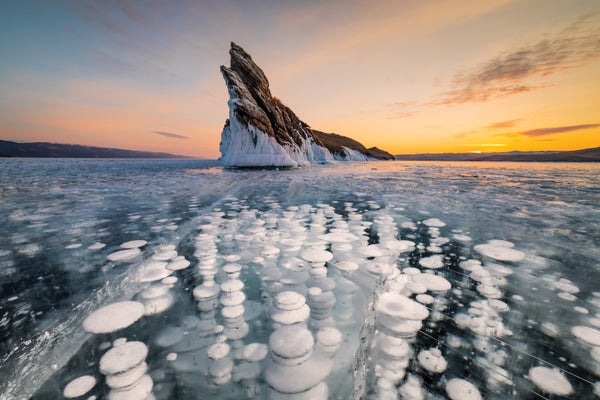
Search intently at an ice cube, and you could place minuscule bubbles formed like teardrops, flattened eggs or even winding worms. Bubble designs in Russia’s Lake Baikal (demonstrated below) are even a lot more vivid. Scientists have identified that ice bubbles’ peculiar shapes can expose how rapid the drinking water froze and how considerably gasoline was dissolved in it, offering essential insights for glaciologists and engineers.
As water freezes, most of its dissolved gases get expelled. But some small bubbles near the freezing edge can get trapped in the solidifying ice, the place they maintain growing. Virgile Thiévenaz, who research fluid mechanics at Paris’s Industrial Physics and Chemistry Larger Education Institute, and Alban Sauret, a mechanical engineer at the University of California, Santa Barbara, re-established this method in the laboratory to tease apart the variables that impact expanding bubbles’ shapes and dimensions.
As Thiévenaz stated in the course of a presentation at an American Physical Society meeting, the scientists observed that ice bubbles are under no circumstances spherical but as an alternative elongate in the way of freezing. The researchers discovered that an ice sample web hosting numerous tiny, somewhat elongated bubbles indicates a superior freezing amount and a higher gas focus, whilst a sample with a few more substantial, extended pores froze more slowly and gradually. These versions are predictable mathematically: “We can match most bubbles with the very same equation,” Thiévenaz suggests. If you know a sample’s freezing level, you can work out the fuel focus, and vice versa. Their equation predicts that very long, cylindrical ice-bubble “worms” will from time to time mature unchecked, weakening the surrounding composition.
On supporting science journalism
If you might be having fun with this report, think about supporting our award-successful journalism by subscribing. By obtaining a membership you are aiding to ensure the upcoming of impactful tales about the discoveries and thoughts shaping our earth currently.
Environmental ice tells a tale about the previous, but analyzing earlier freezing circumstances is difficult. Thiévenaz and Sauret say that earning inferences primarily based on bubble form could be a boon for researchers finding out lake ice and glacier cores. Erin Pettit, a glaciologist at Oregon Condition University, agrees. “I’ve generally been puzzled by the wormy bubbles in pockets of refreezing drinking water within just glaciers,” she suggests. “It’s interesting to see the physics behind their development.”
Also, quite a few engineers favor porous solids for specified programs mainly because of their mild excess weight. By managing gasoline focus and freezing pace, scientists could theoretically dictate a material’s pore shape, foremost to potent and gentle metals, eyeglasses and ceramics, the researchers suggest.