Glow-in-the-Dark Animals Could Have Been Close to for 540 Million A long time
Ancestors of so-referred to as “soft” corals could have made bioluminescence in the earliest days of deep-ocean dwelling
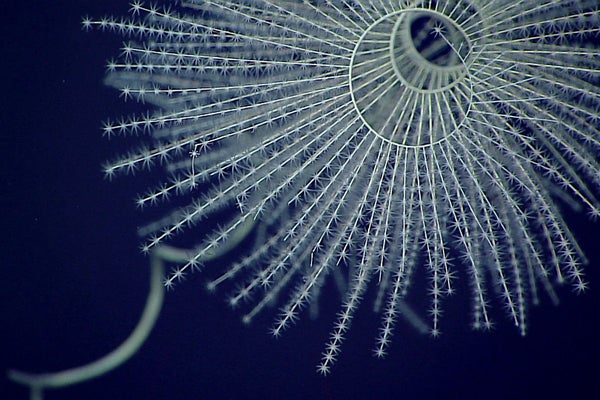
A deep-sea bioluminescent comfortable coral named Iridogorgia magnispiralis.
NOAA Office of Ocean Exploration and Research/Deepwater Miracles of Wake
The a lot more human beings have explored the deep oceans, the far more illustrations we have found of animals with a seemingly magical expertise: the capacity to produce their personal gentle, a feat named bioluminescence.
To experts, the standard existence of bioluminescence would make feeling. It is incredibly prevalent, with a variety of bioluminescence mechanisms having evolved perhaps close to 100 individual periods over the training course of hundreds of tens of millions of many years. And new research published on April 23 in Proceedings of the Royal Culture B traces bioluminescence in the household tree of weird animals named octocorals, a team that consists of “soft corals,” suggesting that the phenomenon evolved in the sea about 540 million years ago—making it far more than two times as previous as a previous estimate.
For animals, in particular these that reside in sections of the oceans that are further than sunlight can reach, bioluminescence can make the change among existence and death: for case in point, it can be utilized as a instrument to lure prey and deter predators, amid other takes advantage of.Biologists are nonetheless working to comprehend the total scope of the phenomenon’s relevance. “We’ve explored so little of our own earth, and there could be so a lot of more organisms down there that are employing light in methods we haven’t even started to comprehend however,” states maritime biologist Edith Widder, CEO and senior scientist at the nonprofit Ocean Research & Conservation Affiliation. “That’s what intrigues me the most about bioluminescence: how animals use it to endure.”
On supporting science journalism
If you happen to be experiencing this posting, take into account supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By paying for a subscription you are serving to to make sure the upcoming of impactful tales about the discoveries and ideas shaping our earth now.
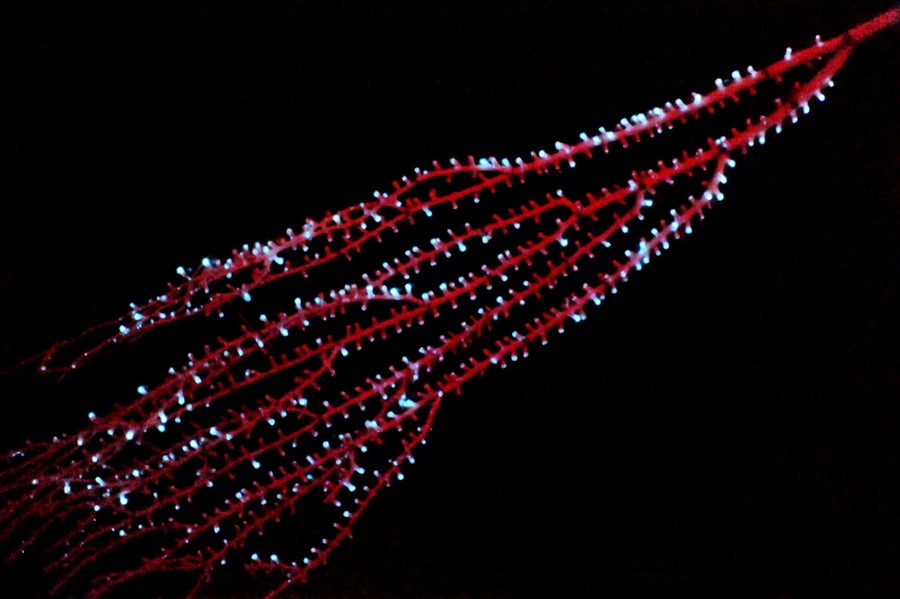
A bioluminescent bamboo coral (a form of smooth coral) named Isidella that was gathered in the Bahamas.
But in spite of its ubiquity these days, bioluminescence that transpired in the earlier is remarkably complicated to research simply because the conduct almost never leaves a trace in fossils—when fossils even exist. Gentle corals, for instance, really don’t form the significant rocklike reefs that we tend to consider of. In its place they build colonies by excreting a gentle construction embedded with tiny chips of skeletonlike content. This life-style signifies that gentle corals depart guiding only the tiniest of fossils, a challenge for researchers who attempt to peer into their histories.
However, Andrea Quattrini, a zoologist and curator of corals at the Countrywide Museum of Purely natural Record in Washington, D.C., and her colleagues wanted to comprehend how—and when—bioluminescence might have formulated in octocorals. Quattrini has expended about a ten years testing dwelling octocorals collected from the ocean to establish no matter if they can generate light by nudging the creatures with a pair of lab tweezers although under a blanket or in a dim space.
In the new analysis, she and her colleagues mapped these outcomes in an evolutionary tree that reveals how distinctive modern-day octocorals are associated to just one one more, allowing the experts to seem for styles in which branches can and can not generate mild. By exploring for the most basic attainable evolutionary tale to match these observations, the scientists concluded that bioluminescence possible evolved just when in these animals. Then they utilised the scarce fossils that scientists have confidently discovered as belonging to individual varieties of octocorals to anchor the tree in time. The analysis indicates the landmark initial acknowledged evolution of bioluminescence in a marine setting occurred some 540 million yrs ago—much older than previous estimates of 267 million a long time in the past.
The new estimate falls just just before or through an occasion that paleontologists have dubbed the Cambrian explosion, when a burst of biological diversification occurred. It’s also all through that time that animals to start with moved from the shallow oceans into the depths the place daylight doesn’t penetrate. This timeline for establishing bioluminescence will make perception, say Quattrini and Widder, who equally note that rudimentary gentle sensors also produced all around this time. In this context, bioluminescence grew to become a communicative tool for corals to use to confuse prey or startle predators away, like “a burglar alarm,” Quattrini states.

A deep-sea bioluminescent octocoral of the genus Iridogorgia (still left). A bioluminescent keratoisidid bamboo coral found in the deep ocean off the coastline of Hawaii (correct).
NOAA Place of work of Ocean Exploration and Research
“I imagine our examine actually details to the fact that it is one of the earliest types of interaction in the oceans—maybe just one of the earliest sorts of conversation on Earth, really,” Quattrini says. “It’s a interesting form of interaction which is seriously very easy at its core.”
Yuichi Oba, a biologist at Chubu University in Japan, who has analyzed bioluminescence but was not concerned in the new research, is additional skeptical. He’d like to see more caution taken with the conclusion that bioluminescence in octocorals didn’t come up independently multiple periods. If it did, that would make the phenomenon additional new than the new analysis suggests—perhaps just 400 million to 200 million years old. Quattrini states that the shared mechanism for bioluminescence across octocorals supports the concept of a solitary evolution.
Quattrini and her colleagues future program to assess the gene that builds the protein liable for bioluminescence in octocorals, a kind of enzyme called a luciferase. The very same gene reveals up in both equally bioluminescent and nonbioluminescent octocorals, she suggests, so the researchers want to fully grasp how some of the animals feel to have misplaced the ability to light-weight up.
And this form of work assists paint a greater photograph of what the ecosystems of the ancient Earth—which appear so alien to us today—may have looked like. “Imagine the ocean in which coral emit gentle and carnivorous predators have significant eyes in midnight drinking water,” Oba says. “Life is fantastic.”